C Programming Foundations
Introduction
Welcome to the world of C programming! In this guide, we'll cover essential concepts and problem-solving techniques that will set the foundation for your journey into the programming realm.
Table of Contents
- Variables
- What are Variables?
- Problem: Calculate Rectangle Area
- Loops
- What are Loops?
- For Loop
- Problem: Factorial Calculation
- While Loop
- Problem: Print N numbers
- Do-While Loop
- Problem: Add numbers entered by user
- Switch...Case
- Problem: Simple Calculator
- Conditional Statements
- What are Conditional Statements?
- if-else statement
- Problem: Leap Year Checker
- if-else ladder
- Nested if-else
- Arrays
- What are Arrays?
- Problem: Largest Element Finder
- Problem: Array Input/Output
- Problem: Calculate average
Variables in C
What are Variables?
In programming, variables are containers that store data. They have a type and a name.
int age; // Declaration
age = 21; // Assignment
char ch = 'a';
ch = 'l';
C is a strongly typed language. This means that the variable type cannot be changed once it is declared. For example:
int number = 5; // integer variable
number = 5.5; // error, can't assign float to int
double number; // error, can't redefine the data type
Problem: Calculate Rectangle Area
Create a program that calculates the area of a rectangle given its length and width.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int length, width;
printf("Enter length: ");
scanf("%d", &length);
printf("Enter width: ");
scanf("%d", &width);
int area = length * width;
printf("Area: %d\n", area);
}
Loops in C
What are Loops?
In programming, a loop is used to repeat a block of code until the specified condition is met.
For Loop
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Code inside the loop
}
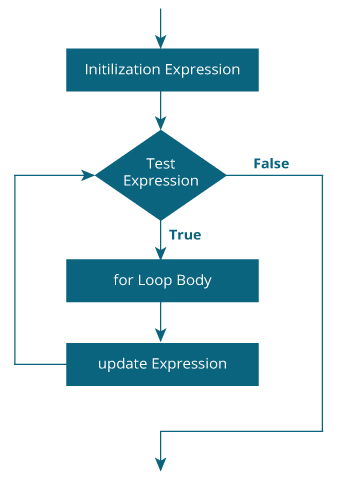
Working of For Loop
Problem: Factorial Calculation
Write a program to find the factorial of a number.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number, factorial = 1;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
factorial *= i;
}
printf("Factorial: %d\n", factorial);
return 0;
}
While loop
The syntax of the while loop is:
while (testExpression) {
// the body of the loop
}
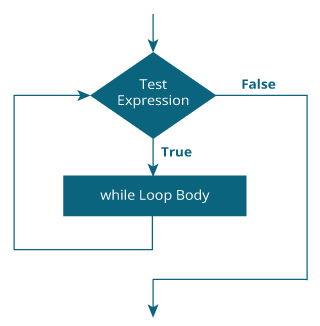
Working of While Loop
Problem: Print N numbers
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int n, i;
// Input the value of n
printf("Enter the value of n: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// Initialize a counter variable
i = 1;
// While loop to print the first n numbers
while (i <= n) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++; // Increment the counter
}
}
Do- While loop
The syntax of the do-while loop is:
do {
// the body of the loop
}
while (testExpression);
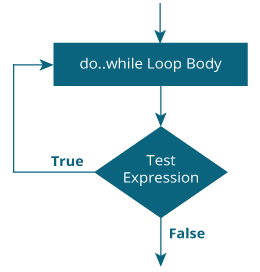
Working of do - while Loop
Problem: Add numbers entered by user
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
double number, sum = 0;
// the body of the loop is executed at least once
do {
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%lf", &number);
sum += number;
}
while(number != 0.0);
printf("Sum = %.2lf",sum);
}
Switch...case loop
The syntax of the switch...case loop is:
switch (expression)
{
case constant1:
// statements
break;
case constant2:
// statements
break;
.
.
.
default:
// default statements
}
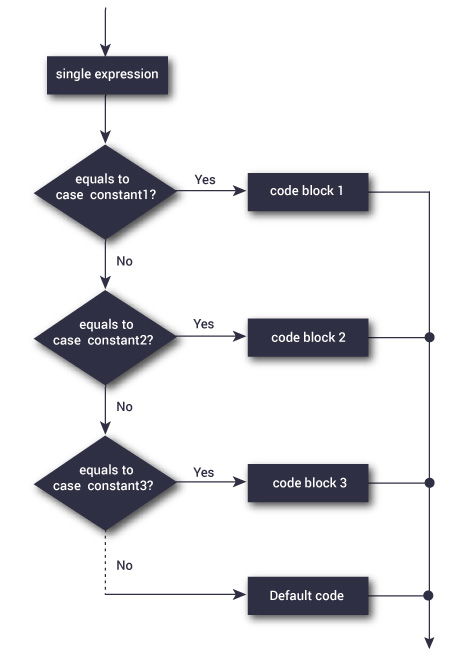
Working of switch...case Loop
Problem: Simple Calculator
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char operation;
double n1, n2;
printf("Enter an operator (+, -, *, /): ");
scanf("%c", &operation);
printf("Enter two operands: ");
scanf("%lf %lf",&n1, &n2);
switch(operation)
{
case '+':
printf("%.1lf + %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1+n2);
break;
case '-':
printf("%.1lf - %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1-n2);
break;
case '*':
printf("%.1lf * %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1*n2);
break;
case '/':
printf("%.1lf / %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1/n2);
break;
// operator doesn't match any case constant +, -, *, /
default:
printf("Error! operator is not correct");
}
}
Conditional Statements in C
What are Conditional Statements?
Conditional statements help your program make decisions.
if-else statement
if (condition) {
// Code to execute if the condition is true
} else {
// Code to execute if the condition is false
}
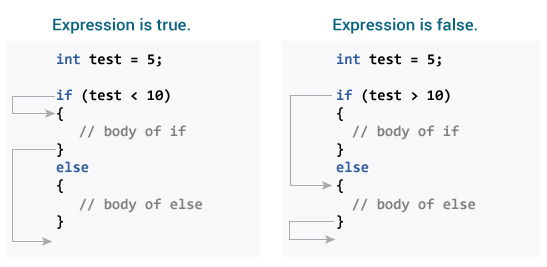
Working of if-else Loop
Problem: Leap Year Checker
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int year;
printf("Enter a year: ");
scanf("%d", &year);
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)) {
printf("Leap year\n");
} else {
printf("Not a leap year\n");
}
}
if-else Ladder
Sometimes, a choice has to be made from more than 2 possibilities.
The if...else ladder allows you to check between multiple test expressions and execute different statements.
if (test expression1) {
// statement(s)
}
else if(test expression2) {
// statement(s)
}
else if (test expression3) {
// statement(s)
}
.
.
else {
// statement(s)
}
Problem: if- else
// Program to relate two integers using =, > or < symbol
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number1, number2;
printf("Enter two integers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &number1, &number2);
//checks if the two integers are equal.
if(number1 == number2) {
printf("Result: %d = %d",number1,number2);
}
//checks if number1 is greater than number2.
else if (number1 > number2) {
printf("Result: %d > %d", number1, number2);
}
//checks if both test expressions are false
else {
printf("Result: %d < %d",number1, number2);
}
return 0;
}
Nested if-else
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number1, number2;
printf("Enter two integers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &number1, &number2);
if (number1 >= number2) {
if (number1 == number2) {
printf("Result: %d = %d",number1,number2);
}
else {
printf("Result: %d > %d", number1, number2);
}
}
else {
printf("Result: %d < %d",number1, number2);
}
return 0;
}
Arrays in C
What are Arrays?
Arrays allow you to store multiple values of the same type under one name.
Syntax
dataType arrayName[arraySize];
//example
int numbers[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};`
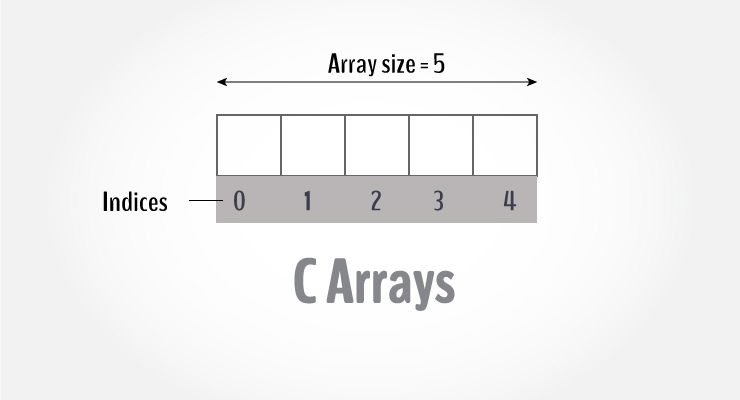
Access Array Elements
You can access elements of an array by indices.
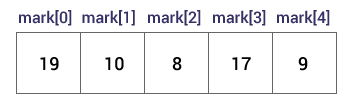
Suppose you declared an array mark as above. The first element is mark[0], the second element is mark[1] and so on.
Problem: Largest Element Finder
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int numbers[] = {12, 45, 67, 23, 9};
int max = numbers[0];
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
if (numbers[i] > max) {
max = numbers[i];
}
}
printf("Largest element: %d\n", max);
}
Problem: Array Input/Output
// Program to take 5 values from the user and store them in an array
// Print the elements stored in the array
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int values[5];
printf("Enter 5 integers: ");
// taking input and storing it in an array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &values[i]);
}
printf("Displaying integers: ");
// printing elements of an array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("%d\n", values[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Problem: Calculate average
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int marks[10], i, n, sum = 0;
double average;
printf("Enter number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("Enter number%d: ",i+1);
scanf("%d", &marks[i]);
// adding integers entered by the user to the sum variable
sum += marks[i];
}
// explicitly convert sum to double
// then calculate average
average = (double) sum / n;
printf("Average = %.2lf", average);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int marks[10], i, n, sum = 0;
double average;
printf("Enter number of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("Enter number%d: ",i+1);
scanf("%d", &marks[i]);
// adding integers entered by the user to the sum variable
sum += marks[i];
}
// explicitly convert sum to double
// then calculate average
average = (double) sum / n;
printf("Average = %.2lf", average);
return 0;
}
Congratulations on completing this C programming foundations! Remember, practice is key to mastering programming. Explore more, solve problems, and enjoy the journey of coding! Happy coding! 😄
