C Programming Foundations
Introduction
Welcome to the world of C programming! In this guide, we'll cover essential concepts and problem-solving techniques that will set the foundation for your journey into the programming realm.
Table of Contents
- Variables
- What are Variables?
- Using Variables
- Loops
- What are Loops?
- For Loop
- Problem: Factorial Calculation
- While Loop
- Problem: Print N numbers
- Do-While Loop
- Problem: Add numbers entered by user
- Switch...Case
- Problem: Simple Calculator
- Conditional Statements
- What are Conditional Statements?
- if-else statement
- Problem: Leap Year Checker
- if-else ladder
- Nested if-else
- Arrays
- What are Arrays?
- Past Year Questions
Variables in C
What are Variables?
In programming, variables are containers that store data. They have a type and a name.
int age; // Declaration
age = 21; // Assignment
char ch = 'a';
ch = 'l';
C is a strongly typed language. This means that the variable type cannot be changed once it is declared. For example:
int number = 5; // integer variable
number = 5.5; // error, can't assign float to int
double number; // error, can't redefine the data type
Using variables
Once a variable has been declared and initialized, you can use it in your program to store and retrieve data. For example, the following code prints the value of the variable age to the console:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age = 25;
printf("My age is %d\n", age);
return 0;
}
Loops in C
What are Loops?
In programming, a loop is used to repeat a block of code until the specified condition is met.
For Loop
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Code inside the loop
}
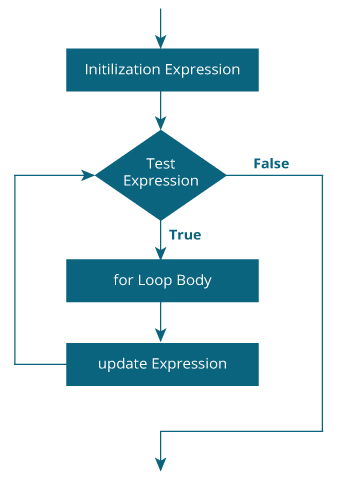
Working of For Loop
Problem: Factorial Calculation
Write a program to find the factorial of a number.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() { // return type int
int number, factorial = 1;
printf("Enter a number: "); //Prints text to console
scanf("%d", &number); //Reads input from console
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
factorial *= i;
}
printf("Factorial: %d\n", factorial);
return 0;
}
While loop
The syntax of the while loop is:
while (testExpression) {
// the body of the loop
}
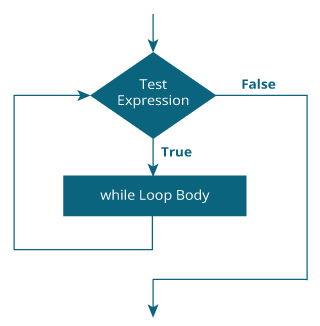
Working of While Loop
Problem: Print N numbers
#include <stdio.h>
void main() { //return type void
int n, i;
// Input the value of n
printf("Enter the value of n: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// Initialize a counter variable
i = 1;
// While loop to print the first n numbers
while (i <= n) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++; // Increment the counter
}
}
Do- While loop
The syntax of the do-while loop is:
do {
// the body of the loop
}
while (testExpression);
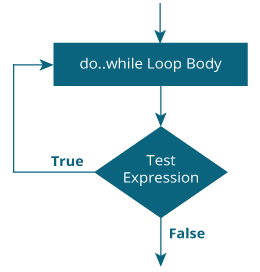
Working of do - while Loop
Problem: Add numbers entered by user
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
double number, sum = 0;
// the body of the loop is executed at least once
do {
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%lf", &number);
sum += number;
}
while(number != 0.0);
printf("Sum = %.2lf",sum);
}
Switch...case loop
The syntax of the switch...case loop is:
switch (expression)
{
case constant1:
// statements
break;
case constant2:
// statements
break;
.
.
.
default:
// default statements
}

Working of switch...case Loop
Problem: Simple Calculator
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char operation;
double n1, n2;
printf("Enter an operator (+, -, *, /): ");
scanf("%c", &operation);
printf("Enter two operands: ");
scanf("%lf %lf",&n1, &n2); //lf reads type "double"
switch(operation)
{
case '+':
printf("%.1lf + %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1+n2);
break;
case '-':
printf("%.1lf - %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1-n2);
break;
case '*':
printf("%.1lf * %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1*n2);
break;
case '/':
printf("%.1lf / %.1lf = %.1lf",n1, n2, n1/n2);
break;
// operator doesn't match any case constant +, -, *, /
default:
printf("Error! operator is not correct");
}
}
Conditional Statements in C
What are Conditional Statements?
Conditional statements help your program make decisions.
if-else statement
if (condition) {
// Code to execute if the condition is true
} else {
// Code to execute if the condition is false
}
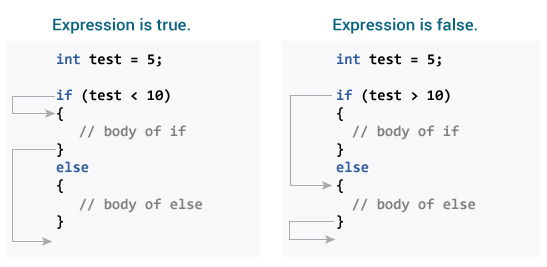
Working of if-else Loop
Problem: Leap Year Checker
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int year;
printf("Enter a year: ");
scanf("%d", &year);
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)) {
printf("Leap year\n");
} else {
printf("Not a leap year\n");
}
}
if-else Ladder
Sometimes, a choice has to be made from more than 2 possibilities.
The if...else ladder allows you to check between multiple test expressions and execute different statements.
if (test expression1) {
// statement(s)
}
else if(test expression2) {
// statement(s)
}
else if (test expression3) {
// statement(s)
}
.
.
else {
// statement(s)
}
Problem: if- else
// Program to relate two integers using =, > or < symbol
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number1, number2;
printf("Enter two integers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &number1, &number2);
//checks if the two integers are equal.
if(number1 == number2) {
printf("Result: %d = %d",number1,number2);
}
//checks if number1 is greater than number2.
else if (number1 > number2) {
printf("Result: %d > %d", number1, number2);
}
//checks if both test expressions are false
else {
printf("Result: %d < %d",number1, number2);
}
return 0;
}
Nested if-else
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number1, number2;
printf("Enter two integers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &number1, &number2);
if (number1 >= number2) {
if (number1 == number2) {
printf("Result: %d = %d",number1,number2);
}
else {
printf("Result: %d > %d", number1, number2);
}
}
else {
printf("Result: %d < %d",number1, number2);
}
return 0;
}
Arrays in C
What are Arrays?
Arrays allow you to store multiple values of the same type under one name.
Syntax
dataType arrayName[arraySize];
//example
int numbers[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};`
Access Array Elements
You can access elements of an array by indices.
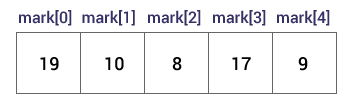
Suppose you declared an array mark as above. The first element is mark[0], the second element is mark[1] and so on.
Past Year Questions 🤩🤩🤩
1) Write a C Program to input size of the array, and then replace each element of the user input array with its reverse. Print the array.
//Solution
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int size;
// Input the size of the array
printf("Enter the size of the array: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
int arr[size];
// Input array elements
printf("Enter %d elements:\n", size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("Enter element %d :",i+1);
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
// Print the original array
printf("Original Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
// Reverse the array in-place
int start = 0;
int end = size - 1;
while (start < end) {
// Swap elements at start and end
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
// Move the start and end pointers
start++;
end--;
}
// Print the array after the reversal
printf("Array After Reversal: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
2) WAP to sort an array A[] consisting of only 1s, 2s, and 3s. the following task needs to be done
- The program should sort the given array and put all 1s first, then all 2s and all 3s in last.
- Print the array elements after sorting.
Test case 1:
Input: {1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3}
Output: {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3}
Test case 2:
Input: {1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 1, 1, 1, 2}
Output: {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3}
//Solution
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int size;
// Input the size of the array
printf("Enter the size of the array: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
int arr[size];
// Input array elements
printf("Enter %d elements (1, 2, or 3):\n", size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
int count1 = 0, count2 = 0, count3 = 0;
// Count the occurrences of 1, 2, and 3 in the array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (arr[i] == 1) {
count1++;
} else if (arr[i] == 2) {
count2++;
} else if (arr[i] == 3) {
count3++;
}
}
// Overwrite the array with the sorted elements
for (int i = 0; i < count1; i++) {
arr[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = count1; i < count1 + count2; i++) {
arr[i] = 2;
}
for (int i = count1 + count2; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = 3;
}
// Print the sorted array
printf("Array After Sorting: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Congratulations on completing this C programming foundations! Remember, practice is key to mastering programming. Explore more, solve problems, and enjoy the journey of coding! Happy coding! 😄
